Learning Objectives
By the end of this activity, students will be able to:
Explain the Doppler Effect in terms of motion and frequency.
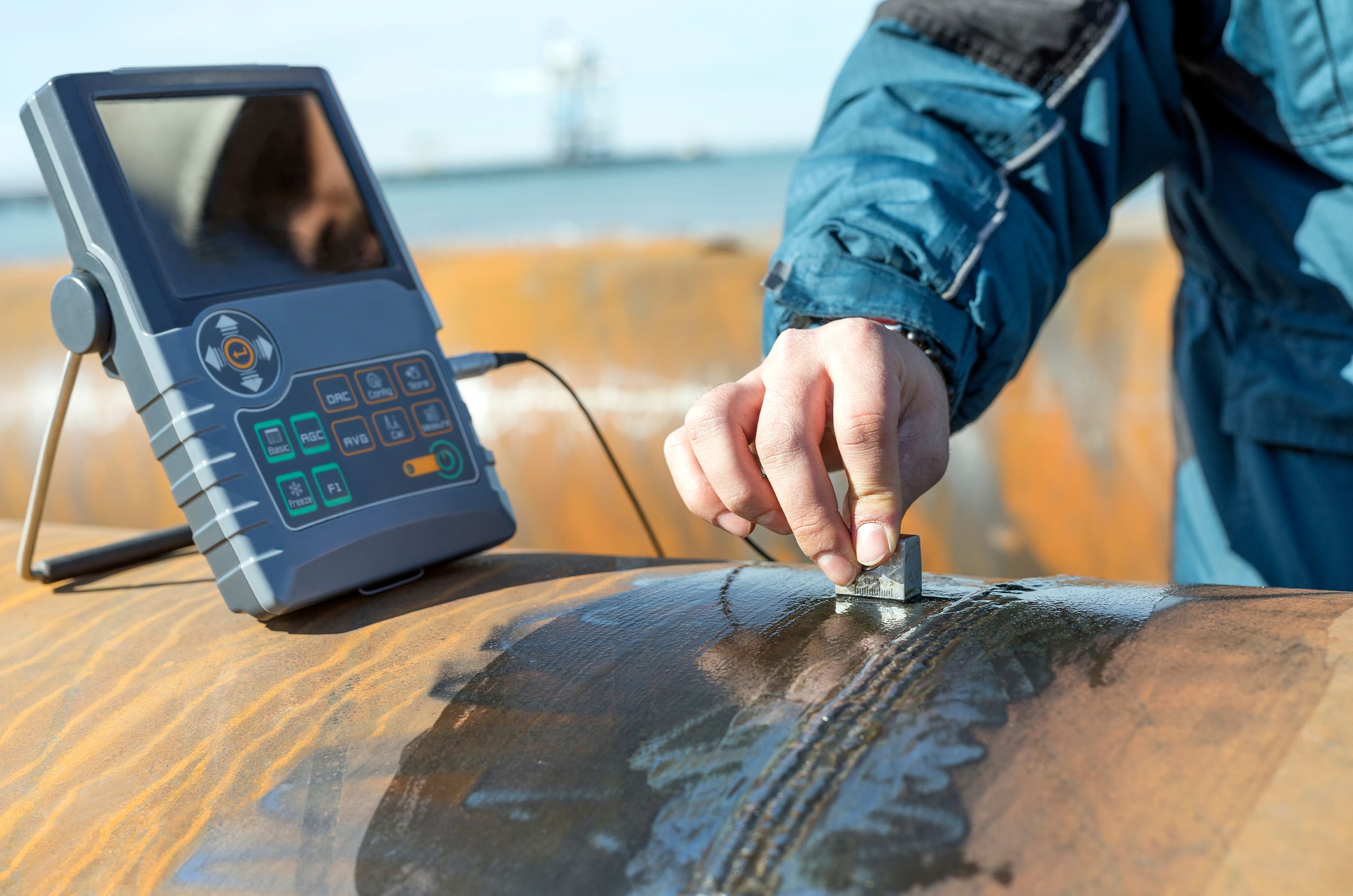
Describe how ultrasonic sound waves are used in NDT.
Observe and interpret changes in pitch related to a moving sound source.
Relate the demonstration to real-world technology (e.g., ultrasound, radar, flaw detection).
Key Concepts
Sound travels in waves.
Frequency increases when a sound source approaches (higher pitch).
Frequency decreases when it moves away (lower pitch).
Ultrasonic waves are sound waves above the range of human hearing (>20 kHz).
In NDT, these waves reflect off internal features, helping technicians "see" inside solid materials.